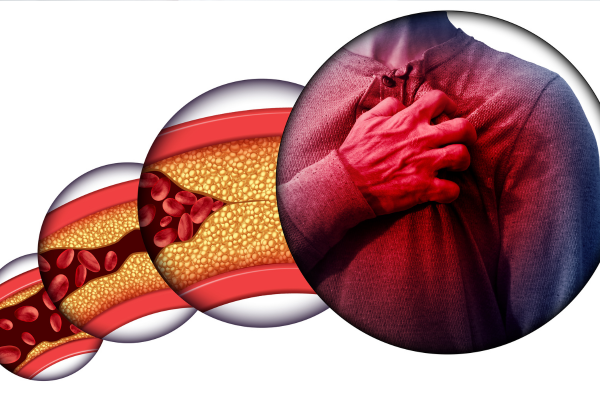
Heart disease remains a leading cause of mortality worldwide, emphasizing the critical importance of
understanding its risk factors and implementing preventive measures. Navigating cardiac health requires
a comprehensive understanding of the various factors that contribute to heart disease, ranging from
lifestyle choices to genetic predispositions. In this comprehensive guide, we delve deep into the
intricate web of heart disease risk factors, empowering readers to make informed decisions about their
cardiovascular health.
Heart disease encompasses a broad spectrum of conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels,
including coronary artery disease, heart failure, and arrhythmias. While some factors, such as age and
family history, are beyond our control, several modifiable risk factors significantly influence heart
health. These include high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, diabetes, obesity, smoking, poor
diet, physical inactivity, excessive alcohol consumption, and stress.
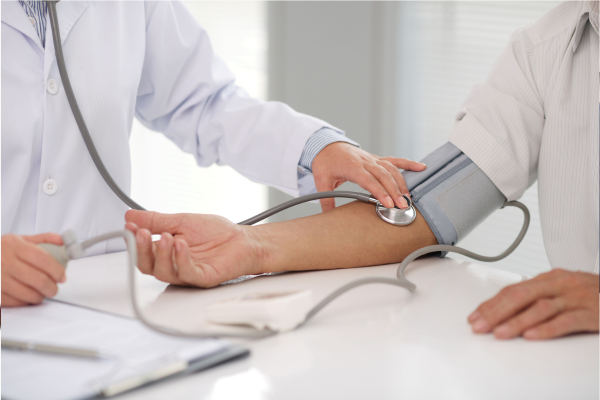
High blood pressure (Hypertension)
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a leading risk factor for heart disease and stroke. It places
increased strain on the heart and blood vessels, contributing to the development of atherosclerosis
(hardening and narrowing of the arteries) and other cardiovascular complications. Managing blood
pressure through lifestyle modifications, such as adopting a heart-healthy diet low in sodium and
saturated fats, regular exercise, weight management, and stress reduction techniques, is crucial for
preventing heart disease.
High cholesterol levels
Elevated levels of cholesterol, particularly low-density
lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, commonly referred to as "bad" cholesterol, can accumulate in the
arteries, forming plaques that obstruct blood flow and increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Adopting a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats (such as those found in nuts,
seeds, and fatty fish) can help lower LDL cholesterol levels. Additionally, regular exercise and
medications, if prescribed by a healthcare provider, may be necessary to manage cholesterol levels
effectively.
Diabetes
Diabetes, especially when poorly controlled, significantly
increases the risk of heart disease. High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels and nerves
that control the heart and blood vessels, leading to complications such as coronary artery disease,
heart attacks, and peripheral artery disease. Managing diabetes through medication, blood sugar
monitoring, a healthy diet, regular exercise, and lifestyle modifications is essential for reducing
the risk of cardiovascular complications.
Obesity
Excess weight, particularly abdominal obesity, is associated
with an increased risk of heart disease, as it contributes to the development of hypertension, high
cholesterol, and diabetes. Adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity are
essential for achieving and maintaining a healthy weight. Incorporating aerobic exercises, strength
training, and flexibility exercises into one's fitness regimen can promote cardiovascular health and
overall well-being.
Smoking
Tobacco use, including cigarette smoking and exposure to
secondhand smoke, is a major risk factor for heart disease. Smoking damages the blood vessels, reduces
oxygen delivery to the heart, and increases the likelihood of blood clots, all of which elevate the
risk of heart attacks and strokes. Quitting smoking is one of the most impactful steps individuals can
take to improve their heart health and reduce their risk of cardiovascular disease.
Ways to prevent yourself from these risk factors!
Diet and nutrition
A heart-healthy diet plays a pivotal role in reducing the risk
of heart disease. Emphasizing whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins,
and healthy fats can help lower blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and promote overall
cardiovascular health. Limiting the intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and foods high in
saturated and trans fats is essential for maintaining heart health. Additionally, incorporating
heart-healthy nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, antioxidants, and potassium into one's
diet can further support cardiovascular wellness.
Physical activity
Regular physical activity is a cornerstone of heart disease
prevention and management. Engaging in aerobic exercises such as walking, jogging, swimming, or
cycling helps strengthen the heart muscle, improve circulation, and lower blood pressure and
cholesterol levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75
minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities
on two or more days a week. Incorporating physical activity into your daily routine not only
benefits your heart but also enhances overall health and well-being.
Stress management
Chronic stress can have detrimental effects on heart health,
contributing to the development and progression of heart disease. Implementing stress management
techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, tai chi, and progressive
muscle relaxation can help alleviate stress and promote relaxation. Prioritizing self-care,
maintaining a healthy work-life balance, and fostering supportive relationships are also integral
components of stress management. By managing stress effectively, individuals can safeguard their
heart health and reduce their risk of cardiovascular complications.
Regular health check-ups
Regular health check-ups and screenings are essential for
monitoring heart health and detecting potential risk factors or underlying conditions early.
Schedule regular visits with your healthcare provider to assess blood pressure, cholesterol levels,
blood sugar levels, and other key indicators of heart health. Depending on your age, medical
history, and risk factors, your healthcare provider may recommend additional tests such as an
electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram, stress test, or coronary calcium scan to evaluate heart
function and assess cardiovascular risk.
Collaborative care
Effective management of heart disease often requires a
multidisciplinary approach involving various healthcare professionals, including cardiologists,
primary care physicians, dietitians, exercise physiologists, and mental health professionals.
Collaborative care ensures comprehensive evaluation, personalized treatment plans, and ongoing
support for individuals with heart disease. By working closely with your healthcare team and
actively participating in your care, you can optimize outcomes and improve your quality of life.
Navigating cardiac health is a lifelong journey that requires commitment, awareness, and
proactive engagement. By understanding the modifiable risk factors for heart disease and
implementing evidence-based strategies for prevention and management, individuals can reduce their
risk of cardiovascular complications and enjoy better heart health. Empowered with knowledge and
equipped with actionable tools, we can navigate the complexities of cardiac health and embark on a
path towards lifelong cardiovascular wellness.